Periodontal (Gum) Disease – What is it and How do we treat it?
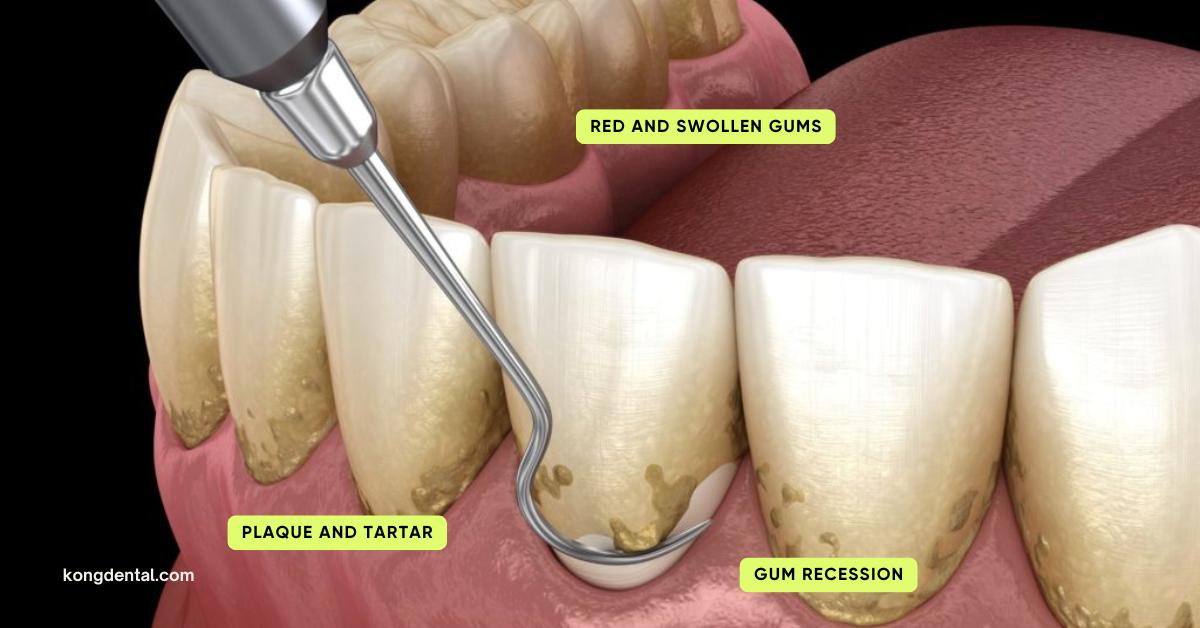
“My gums bleed sometimes when I’m brushing, but they don’t hurt – should I be worried?”
In Singapore, a whopping 90% of adults suffer from gum disease. It starts off as gingivitis, before developing into the more severe and advanced form – periodontitis. This condition tends to go unnoticed, as it can sometimes be painless and the only signs you have a gum problem is a bit of blood in the sink when you brush your teeth.
Untreated gum disease can lead to acute and chronic gum infections and ultimately lead to loss of teeth even in the absence of decay without timely intervention by a dentist. Hence, there is great importance in knowing what exactly gum disease is, and how we can prevent or treat it.
Types of Gum Diseases
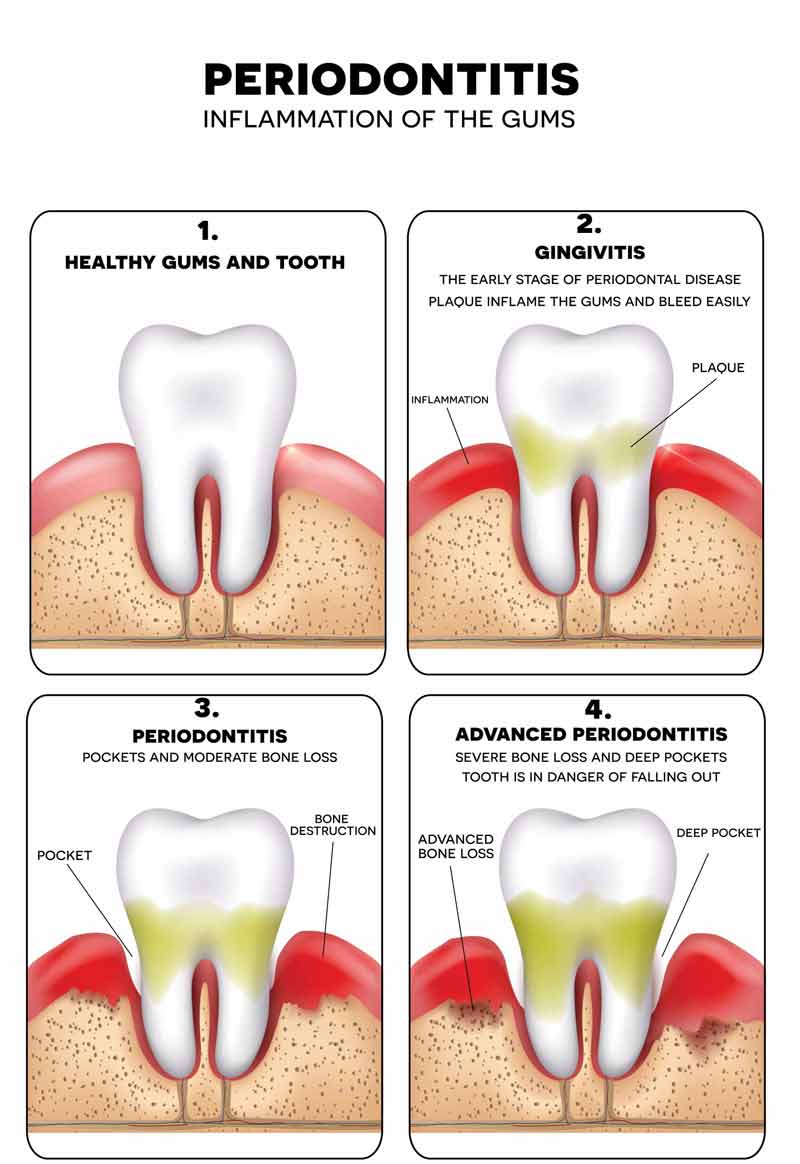
Gum disease presents itself in two different forms: periodontitis and gingivitis. Periodontitis develops from gingivitis and is the more severe form of gum disease – below, we explore each disease and how they are treated.
Gingivitis: The Early Stage of Gum Disease
Gingivitis refers to inflammation of the gums, a condition that happens when there is plaque buildup on the teeth resting against the gums. This is the earliest stage of gum disease and is also the most common and prevalent form of it.
Most individuals would have had gingivitis at some point in their lives. Fortunately, it is an easily treatable condition if managed early; periodic checkups with your dentist are therefore essential to identifying and managing it before it progresses to the more severe form, periodontitis.
Signs and symptoms of gingivitis:
You may be suffering from gingivitis if you experience the following:
- Gums that easily bleed before and after tooth brushing or flossing
- Swollen, puffy, and tender gums
- Deep red colouration of the gums
- Gum recession
- Bad breath
- Blood on the pillow after waking up
Gingivitis is commonly referred to as a silent disease as it is usually painless, although in rarer circumstances it can exhibit soreness or pain.
Afraid of pain? Read more: Pain free dental clinics in Singapore.
What causes gingivitis?
The primary cause of gingivitis is plaque. Plaque is a sticky yellow substance that forms on our tooth surfaces, beginning 4-12 hours from our last brush. Improper brushing techniques, not flossing or forgetting to brush at regular intervals lead to plaque buildup. The bacteria in plaque sitting against the teeth trigger an inflammatory reaction from the body as a protective mechanism, resulting in the characteristic puffy and red presentation of the gums.
Plaque that has not been cleared for a substantial amount of time tends to calcify into calculus, a hard yellow deposit that acts as a perpetual plaque and bacteria trap. Calculus cannot be removed with brushing alone and requires a dental professional to clean it off.
How do we treat gingivitis, and can we prevent it?
Gingivitis is a reversible disease. Good oral hygiene will reduce the rate and amount of plaque buildup, reducing inflammation and allowing the gums to recover and ‘tighten’ around the teeth. Healthy gums are pink, flush against the teeth and do not bleed easily or hurt whilst being brushed.
Continuing to maintain a good level of oral hygiene will
Interdental cleaning is also important – the spaces in between teeth easily trap plaque and food, making it even more susceptible to gingivitis and decay. The use of floss or interdental brushes helps to dislodge this food and debris.
Your dentist will treat this problem by:
- Doing a general scale and polish to remove calculus and tartar
- Adjusting restorations that may have plaque-trapping areas
- Providing oral hygiene instruction and targeted advice on effective plaque removal for your dentition, especially for more complicated cleaning such as under bridges or around implants
- Monitoring the recovery of your condition to see if it does not progress to periodontitis
Periodontitis: Severe Stage of Gum Disease
Periodontitis is a serious gum infection that causes the gums to pull away from the teeth and leads to tooth loss. This is among the prevalent threats to dental health. It can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, or coronary disease if left untreated.
Periodontal disease is an infection in the tissues surrounding the teeth that leads to the loss of bone around the teeth.
It is a type of gum disease caused by bacteria. Gum disease leads to the gradual loss of the bone around the teeth, which is necessary to hold the teeth in place in the mouth.
Most cases of periodontitis occur in adults, especially those who smoke or have diabetes. Periodontitis is more likely to develop if you have poor oral hygiene and dietary habits.
Below is an illustration of how gingivitis advances to periodontitis.
What are the risk factors of periodontitis?
Here are some factors that may increase your risk of developing periodontitis:
- Having gingivitis
- Poor oral hygiene
- An unhealthy diet containing excessive amounts of sugar and processed foods
- Consuming low amounts of vitamins (especially vitamin C) and minerals
- Not chewing properly your food
- Consuming tobacco products and alcoholic drinks
- Hormonal changes related to pregnancy or menopause
- Obesity
- Genes (If your parents suffered from gum diseases, you are more likely to get them as well)
- Not flossing
- Medications that cause dry mouth
- Diseases such as diabetes, Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis
- Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as cancer, leukaemia, and many others
Can severe periodontitis be treated?
It is possible to require gum surgery in severe cases of periodontitis, which involves deep cleaning of the gums and teeth.
With deep cleaning, a periodontist involves the use of two methods – scaling and root planning.
During scaling, tartar is scraped off above and below the gum line using a laser. On the other hand, root planning involves removing the rough spots on the roof of the teeth, which eliminates bacteria causing periodontitis.
Is periodontitis preventable?
Although periodontitis is among the most common chronic gum disease, it is still highly preventable.
The best way to protect your gums from gum diseases is to maintain a healthy lifestyle and good oral hygiene habits. Follow these tips to protect your gums from the risk factors for developing gum diseases.
- Cut down on sugary foods and drinks. Start by cutting down on sugary food and drinks such as cookies, candy, and soda. Sucrose is linked to the onset of gingivitis, a precursor to periodontitis.
- Eat more vegetables. Vegetables and fruits are rich in vitamins and minerals essential to strengthen your teeth and gums and prevent gum diseases.
- Brush your teeth twice daily. By brushing your teeth twice a day, you can prevent gum disease. To prevent and control plaque, brush your teeth 30 minutes before bedtime.
- Floss your teeth. By flossing once a day, you remove bacteria and food particles trapped between your teeth and gums. In fact, brushing your teeth does not remove enough of these harmful substances.
- Get a regular dental check-up and cleaning. To detect and treat gum diseases at an early stage, it is crucial to see the dentist once every six months.
Read more about: Top 5 Reasons To Visit A Dentist
Why Maintaining Good Gum’s Health is Essential?
Most people think good oral hygiene is enough to keep gums healthy and prevent periodontal disease. However, there is more to it than that. It is important to maintain healthy gums for a healthy smile, to prevent decay, and to prevent other oral diseases such as periodontitis from occurring.
- Preventing Decay. Periodontal disease can damage the bone that supports your teeth, making them loose over time. When the supporting bone is gone, the teeth will become loose, and you will need to have them removed. Hence, it is crucial to prevent gum diseases to maintain a healthy smile.
- Preventing tooth loss. In extreme cases, not treating the infection in time can even result in tooth loss. Bacteria can spread to the root of the tooth and destroy the surrounding tissues. In some cases, even a root canal might not be effective anymore. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain good gum health to prevent tooth loss.
- Reducing the risk of other oral diseases. Gum diseases are also linked to other oral diseases such as oral cancer, heart disease and stroke. Therefore, to reduce the risk of contracting other oral diseases, you need to maintain good gum health.
The Bottom Line
Gum disease is a serious issue that can lead to tooth loss and other oral health issues if left untreated. While brushing and flossing regularly can help prevent gum disease, unhealthy habits can increase your risk of developing gum disease. To protect your gums from gum diseases, follow a healthy diet, brush, and floss your teeth regularly, and visit your dentist for a check-up at least once in every six months.
Need a gum specialist in Singapore? At Kong Dental, you can find a professional gum doctor that can perform thorough periodontal screenings and recommend treatment whenever necessary. Book an appointment today!
Please feel free to call our clinic at:
- Choa Chu Kang Dental Clinic – Call +65 6769 5833
- Dental Clinic Yew Tee – Call: +65 6767 9502
- Jurong East Dental Clinic – Call +65 6251 3098
- Dental Clinic Teck Whye Lane – Call +65 6219 5898
- Sunshine Place Dental Clinic – Call +65 6493 2587
Book an appointment with a Licensed Dentist in Singapore Today!
Make An Enquiry
Let us know your concerns and our clinic staff will get back to you in 1-2 hours.
Prefer to talk to our clinic staff directly? Call our clinic to chat with our friendly nurses at +65 6767 9502
General Information
-
Yew Tee Point
21 Choa Chu Kang North 6 #01-27 Singapore 689578
Tel: +65 6767 9502
(Please Enter The Clinic From Outside The Mall) -
Consulting Hours
Mon to Fri: 9AM to 9PM
Sat: 9AM to 6PM
Sun and PH: Closed

